As per current trends and reports, 41% of adult users use voice search at least one time a day. This means that the use of voice AI is steadily on the rise.
A significant contributor to the upward trend in voice searches among customers is the advent of smart home devices. By ensuring that the responsive voice coming from the smart home devices remains human-like and provides an empathetic experience, users are more inclined to interact with services such as chatbots.
In a detailed report published by the American Psychological Association (APA), data shows that even though technology has increased the number of communication channels between users, voice is still preferred. This is because voice AI lends a more intimate experience to interactions and helps create stronger bonds.
How do voice bots and chatbots work?
Conversational artificial intelligence (AI) is a software solution used by business houses and other chatbot users to engage with customers through email-based bots, chatbots or voice bots. Voice bots interact with customers by analyzing their vocal data and formulating the most accurate response by encoding and decoding spoken content. With the help of machine learning, the system can train itself to continuously improve its accuracy and provide better service.
On the surface, the use of chatbots might seem very linear. However, various components go into this technology to ensure accuracy and speed.
Various Components of Voice Bots
Automatic speech recognition (ASR): The backbone of voice bots
Automatic speech recognition or ASR forms the backbone of voice bots, as it’s directly responsible for converting spoken verbatim data into text. When a customer speaks to an AI bot, a chatbot or a voice assistant, the ASR component uses an audio feed to transcribe the voice message into a wav file. The wav file is then filtered by removing background noises and other disturbances, to provide a smoother experience to the customers, after which it is then broken down into phonemes. Phonemes basically define how words sound, and by linking that data together, the ASR can deduce what the customer has said.
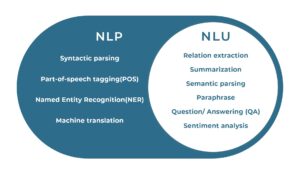
Natural language understanding (NLU) for voice and text-to-speech bots
Natural language understanding (NLU) is a sub-branch of the larger topic of natural language processing (NLP). NLP deals with the entire spectrum of functionality for voice bots, where it interprets input data, deciphers the meaning and formulates responses for the users. NLU plays a vital role in this process, by helping the algorithm identify intent and tone within a short time. In other words, NLU helps the AI-powered virtual chatbot assistant distinguish conversational elements and take the business interaction forward.
Voice bot conversation module for correct responses
A well-defined conversation module allows users to effortlessly interact with the voice bot service without having to follow a directive course (like in the case of IVR systems). The entire style and experience of interaction revolves around the user’s service requirement and intent, and subsequently retrieving relevant information to help the user.
Text-to-speech AI voice bots system
Text-to-speech or TTS is the business component that ‘reads aloud’ the text data that is visible on a computer screen or digital interface. In other words, the system uses various deep learning techniques over time to read a response and mimic a human voice when reading it aloud to the customer. When the NLP-NLU component analyses the input data from a user, it formulates a relevant service response that is fed into the TTS component. The output from the TTS is what the customer hears and experiences.
How do voice bots comprehend complex languages and accents?
Global adoption of voice-based technologies has established ‘voice’ as a preferred business service medium amongst customers, and the numbers and data speak for themselves. However, a common roadblock that most conversational AI solution providers endure is the process of training their interactive voice bot for the optimum user engagement and experience.
Today, there are over 7,000 different languages and dialects. Yet, this isn’t the real problem. If we were to take one single language, we’d soon learn that this one language is spoken differently across the world.
The English language is the biggest example of this problem. English is spoken across all 195 countries in the world and has over time grown to be the official or business language for 67 of them. That means there are over 100 different accents for the English language alone! For each accent, there are a definitive set of phonemes that makes it difficult for the AI-powered voice bots, chatbots and text-to-speech bots to comprehend.
With the help of voice AI for speech recognition optimization
Speech recognition optimization is a branch of computer science that deals with the business of computational linguistics. It helps the AI understand specific languages and accents by benchmarking them against an existing database of knowledge. With the help of a voice biometrics solution, the AI can, in very little time, identify the customer’s accent to begin processing conversational input.
By implementing pre-trained multilingual AI voice bot speech encoders
With the help of modern machine learning models, text-to-speech bots can be trained with billions of customer conversations to help create a strong foundation for the NLP component. For example, Gnani.ai is continuously strengthening its foundation by training its model in 20+ international languages to broaden its service of customer experience. As opposed to building new models for multiple languages, we can now deploy any language on-demand in a few days or within very less time.
By utilizing a multilingual AI voice bot value extractor
Value extraction and its degree of data service accuracy could make or break your customer experience (CX) goals. When a customer interacts with an AI voice bot, certain crucial values regarding name, address, reference numbers etc., are extracted irrespective of the language used. If a user is talking to an AI voice assistant in French, crucial values might be in English (age, phone number). Hence, the value extractor must be trained to analyze languages and decipher critical business data.
What lies ahead with AI, voice and text-to-speech bots?
The global market size of AI-powered virtual assistants will be worth a business of over USD 1.3 billion by the end of 2024, and trends point towards voice-based assistants owning over 50% of this service share. Hence, it’s clear that the power of ‘voice’ will take over business processes and customer engagement initiatives and voice bot experiences.
If you’re interested in learning more about how you can leverage AI and voice bot service for your business, talk to us any time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI voice bot?
Voice bots are software powered by artificial intelligence (AI) that enable a caller to navigate an interactive voice response (IVR) system with their voice using natural language generally. Callers don’t have to listen to the menus and press corresponding numbers on their keypads.
What are the examples of voice bot?
Some common examples of voice bots are Amazon Alexa, Apple’s Siri and Google Assistant.
Click here to check out Gnani.ai’s voice solutions.





